Anxiety
Anxiety, once a whisper, grows loud with time, distorting life’s rhythm, turning worry to crime, a shadow on mind and body entwined.

Anxiety is a healthy emotion but it becomes a problem only when a person starts to feel disproportionate levels of anxiety regularly, it might turn into a medical condition. Anxiety disorders are a group of mental health conditions characterized by intense and excessive feelings of nervousness, fear, apprehension, and worry. Mellow anxiety is vague, while severe anxiety can affect a person’s normal life. These disorders can degrade how a person understands their emotions and behaviors and this might cause physical symptoms as well.
Table of Contents
Anxiety disorder affects a large portion of the population An estimated 301 million people, or you can say 4% of the global population suffer from an anxiety disorder. This makes anxiety disorders the most common mental disorder.
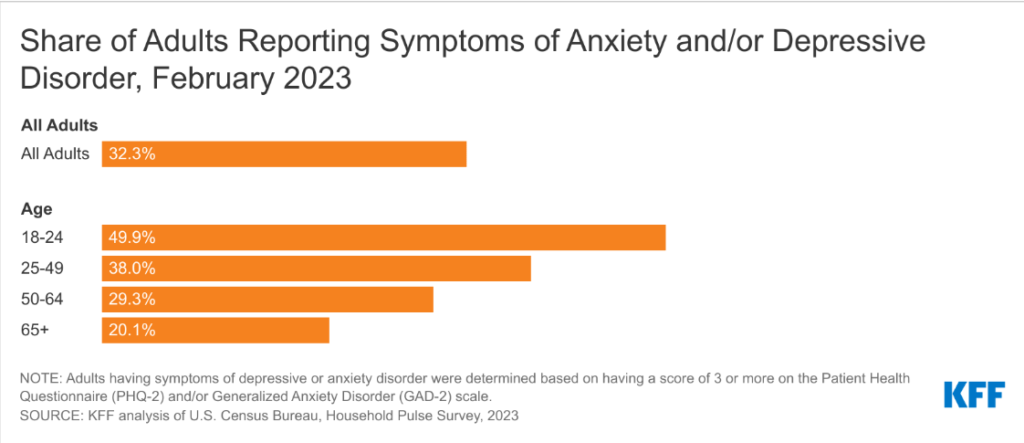
The COVID-19 pandemic had a major impact on the mental health of people and anxiety and depressive disorders grew from 298 million to 374 million, which is a 25% increase. Despite the effective treatments being readily available, only 27.6% of people with anxiety disorders receive treatment.
Anxiety disorders affect 40 million people in the United States and According to a 2023 study, 0.57% of the population of India has generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). This means that approximately 7.3 million. However, only 36.9 percent of people receive treatment.
The COVID-19 pandemic had a major impact on the mental health of people and anxiety and depressive disorders grew from 298 million to 374 million, which is a 25% increase. Despite the effective treatments being readily available, only 27.6% of people with anxiety disorders receive treatment.
Anxiety disorders affect 40 million people in the United States and According to a 2023 study, 0.57% of the population of India has generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). This means that approximately 7.3 million. However, only 36.9 percent of people receive treatment.
What is Anxiety?
The definition of Anxiety given by the American Psychological Association (APA) is “an emotion characterized by feelings of tension, worried thoughts, and physical changes like increased blood pressure.”
If you know the difference between normal anxiousness and an anxiety disorder that requires medical attention, it can help a person understand and treat the condition. In this article, we will understand what separates normal anxiety from anxiety disorders, the several forms of anxiety, and the available treatment options.
We know that anxiety can cause distress but it is not always a medical condition. So when does Anxiety need treatment? To get this answer let’s understand it from the basics.
If you know the difference between normal anxiousness and an anxiety disorder that requires medical attention, it can help a person understand and treat the condition. In this article, we will understand what separates normal anxiety from anxiety disorders, the several forms of anxiety, and the available treatment options.
We know that anxiety can cause distress but it is not always a medical condition. So when does Anxiety need treatment? To get this answer let’s understand it from the basics.
Anxiety
It occurs when an individual faces potentially harmful or worrying triggers, and this feeling is not just natural but it is also necessary for your survival. From the beginning of humanity, our body sets off alarms whenever predators and incoming danger approaches. The body displays These alarms as a raised heartbeat, sweating, and increased sensitivity to surroundings.
Sensing a danger causes a rush of adrenaline, the hormone that acts as a chemical messenger for the brain, and the brain in turn triggers the anxious reaction—popularly known as the “fight-or-flight” response. It prepares a person to confront or escape potential threats.
Nowadays, protecting yourself from large animals or imminent danger is less of a priority than it was for early humans. In the current times, people have anxiety relating to life, health, family, work, money, and other crucial issues that require an individual’s attention without the indispensable need for a “fight-or-flight” reaction.
The nervousness you experience before a big moment in your life or a difficult situation is the natural echo of the old and gold “fight-or-flight” reaction. At the same time, it can still be essential for survival in instances like having the anxiety of being hit by a car while crossing the road. In this situation, a person will instinctively look left and right to avoid danger.
Sensing a danger causes a rush of adrenaline, the hormone that acts as a chemical messenger for the brain, and the brain in turn triggers the anxious reaction—popularly known as the “fight-or-flight” response. It prepares a person to confront or escape potential threats.
Nowadays, protecting yourself from large animals or imminent danger is less of a priority than it was for early humans. In the current times, people have anxiety relating to life, health, family, work, money, and other crucial issues that require an individual’s attention without the indispensable need for a “fight-or-flight” reaction.
The nervousness you experience before a big moment in your life or a difficult situation is the natural echo of the old and gold “fight-or-flight” reaction. At the same time, it can still be essential for survival in instances like having the anxiety of being hit by a car while crossing the road. In this situation, a person will instinctively look left and right to avoid danger.
Anxiety Disorders
When the severity or the duration of the anxious feeling is way out of proportion as compared to the actual stressor or the trigger causing physical symptoms such as increased blood pressure and nausea. These move beyond anxiety and now can be classified as Anxiety disorder.
Symptoms
General Anxiety Disorder(GAD) often consists of these symptoms:-
- A sense of unease and constant tension
- Uncontrollable feelings of worry
- Increased irritability
- Concentration difficulties
- Sleep difficulties, such as difficulty in falling or being asleep
GAD may occur as a vague, unsettling worry or a much more intense form of anxiety that disrupts your daily living. While the symptoms mentioned above can be normal to experience in day-to-day life, people who have GAD will experience it at a more chronic or extreme level.
Types
In the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Health Disorders: Fifth Edition (DSM-V) anxiety disorders have been classified into several main types and here are some of them.
Earlier in the DSM, the list of anxiety disorders included obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and also acute stress disorder. Now, the manual does not group these mental health difficulties under anxiety.
The list of anxiety disorders now includes the following:
Earlier in the DSM, the list of anxiety disorders included obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and also acute stress disorder. Now, the manual does not group these mental health difficulties under anxiety.
The list of anxiety disorders now includes the following:
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD):- A recurrent disorder that involves extreme and long-lasting anxiety and worries relating to unclear life events, objects, and situations. GAD is one of the most common anxiety disorders, and the people who suffer from it are not usually able to find out the cause of their anxiety.
- Panic Disorder: Sudden and intense feelings of worry and fear are experienced by people with panic disorder. These attacks can cause shaking, confusion, dizziness, nausea, and difficulty in breathing. Panic attacks occur suddenly and quickly start getting worse and reach their peaks in under 10 minutes. However, a panic attack can last for hours.
- Specific Phobia: This is an irrational fear and avoidance of a particular object or situation. Phobias are different from other anxiety disorders, as they relate to a specific cause. A person with a phobia might acknowledge fear as irrational or extreme but remain unable to control feelings of anxiety around the trigger. The phobia could be triggered by anything ranging from any situation to any object or even an animal.
- Agoraphobia: Fearing and avoiding places, events, or situations that may be difficult to escape or help would not be there if the person feels trapped. People often misunderstand this condition as a fear of open spaces and the outdoors, but it is not that simple. A person with agoraphobia might fear leaving home or using elevators and public transport.
- Selective Mutism: This is a type of anxiety that some children experience, in which they cannot speak in certain places or settings, like school, even though they might have excellent verbal communication skills around familiar people. It could be an extreme form of social phobia.
- Social Anxiety Disorder: It is the concern about being judged by others during social interactions or the worry of being publicly embarrassed. Social anxiety includes a wide range of feelings including stage fear, fear of intimacy, fear of humiliation and rejection, etc, and these feelings are often more intense and persistent than those experienced by most people. People who have this disorder tend to avoid public situations and human contact to the point that everyday living is rendered extremely difficult.
- Separation Anxiety Disorder: It is characterized by excessive anxiety related to separation from attachment figures like a person or a place which leads to insecurity and fear. The separation might sometimes result in panic symptoms.
Causes
The causes of anxiety disorders are complex. Many factors could happen simultaneously, some might lead to others, and some might not lead to an anxiety disorder unless another is present.
Possible causes include:
Possible causes include:
- Environmental stressors: Such as workplace difficulties, problems in a person’s relationships, or maybe family issues.
- Genetics: People who have members in their family with an anxiety disorder are more likely to experience one themselves too.
- Medical factors: The symptoms of a different disease, the effects of a medication, or the stress of an intensive surgery or prolonged recovery.
- Brain chemistry: Many anxiety disorders are defined as misalignments of hormones or electrical signals in the brain by psychologists.
- Withdrawal from an illicit substance: When someone stops using an addictive substance, they might experience withdrawal symptoms. These symptoms can make existing problems or conditions, such as mental health issues or physical illnesses, feel much more severe or intense.
Treatment
The treatment can include everything from psychotherapy to behavioral therapy and also medications.
- Alcohol Dependence: Someone with this condition will often need treatment for an alcohol or drug problem.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): This type of therapy aims to recognize and change the patterns of thought and beliefs that are associated with and trigger anxiety symptoms.
- Medication: A person can support and maintain their physical health with medications such as antidepressants, benzodiazepines, tricyclics, and beta-blockers.
- Counseling: This is a common treatment for anxiety. It involves talking with a qualified mental health professional who can help a person identify and address the root cause of their anxiety.
These carefully selected products can support you on your journey to overcoming anxiety.
Unwynnd Stress Balls
Clefairy Desktop Punching Bag
Try a Weighted blanket that suits you the best
A Fitness band can help you stay consistent as well
Kampes Cool Mist Aroma Diffuser
“This is an affiliate link. See the full disclaimer in the footer at the end of this page”
Conclusion
Anxiety is one form of stress response but becomes quite problematic when it converts into an overwhelming disorder. Millions worldwide are affected, and its symptoms and forms range from GAD, and panic disorder, to social anxiety. Its causes are numerous, running from genetics to environmental stresses, but the treatments that work include therapy, counseling, and medication. Understanding the difference between normal anxiety and disorders sets the way for effective management of anxiety and improvement of mental health. Early diagnosis and treatment can go a long way in significantly enhancing quality of life.
If you found this information helpful, share it with those who might need it. Understanding your anxiety is one of the first steps to managing it. Remember, seeking help is a sign of strength, and there are many resources available to support those struggling with anxiety. Stay informed, stay supported, and take care of your mental health.
If you found this information helpful, share it with those who might need it. Understanding your anxiety is one of the first steps to managing it. Remember, seeking help is a sign of strength, and there are many resources available to support those struggling with anxiety. Stay informed, stay supported, and take care of your mental health.
References and Resources
The information in this blog is for educational purposes only and is supported by the sources referenced. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a qualified healthcare professional before making any changes to your health routine. We do not take responsibility for any outcomes based on the information provided.


